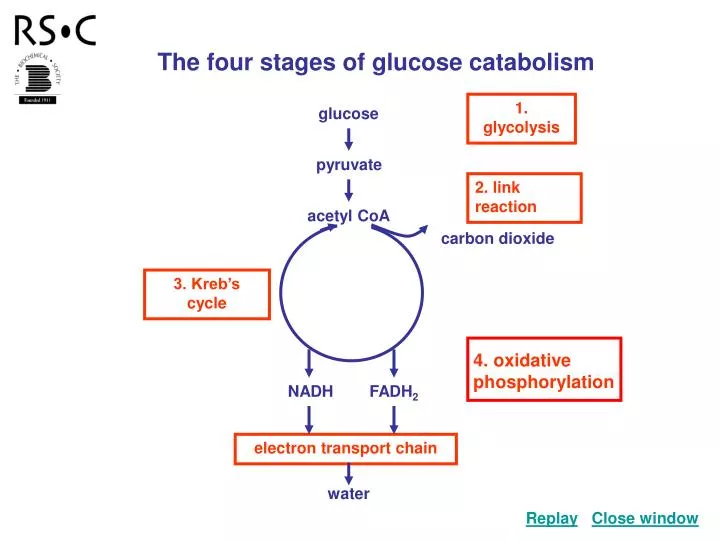
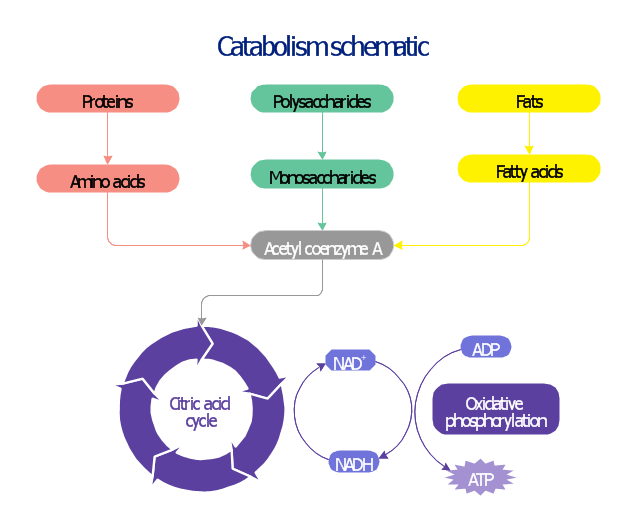
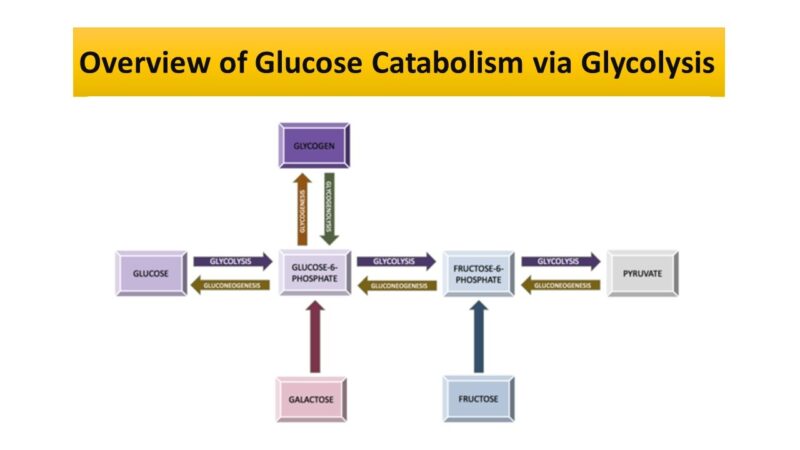
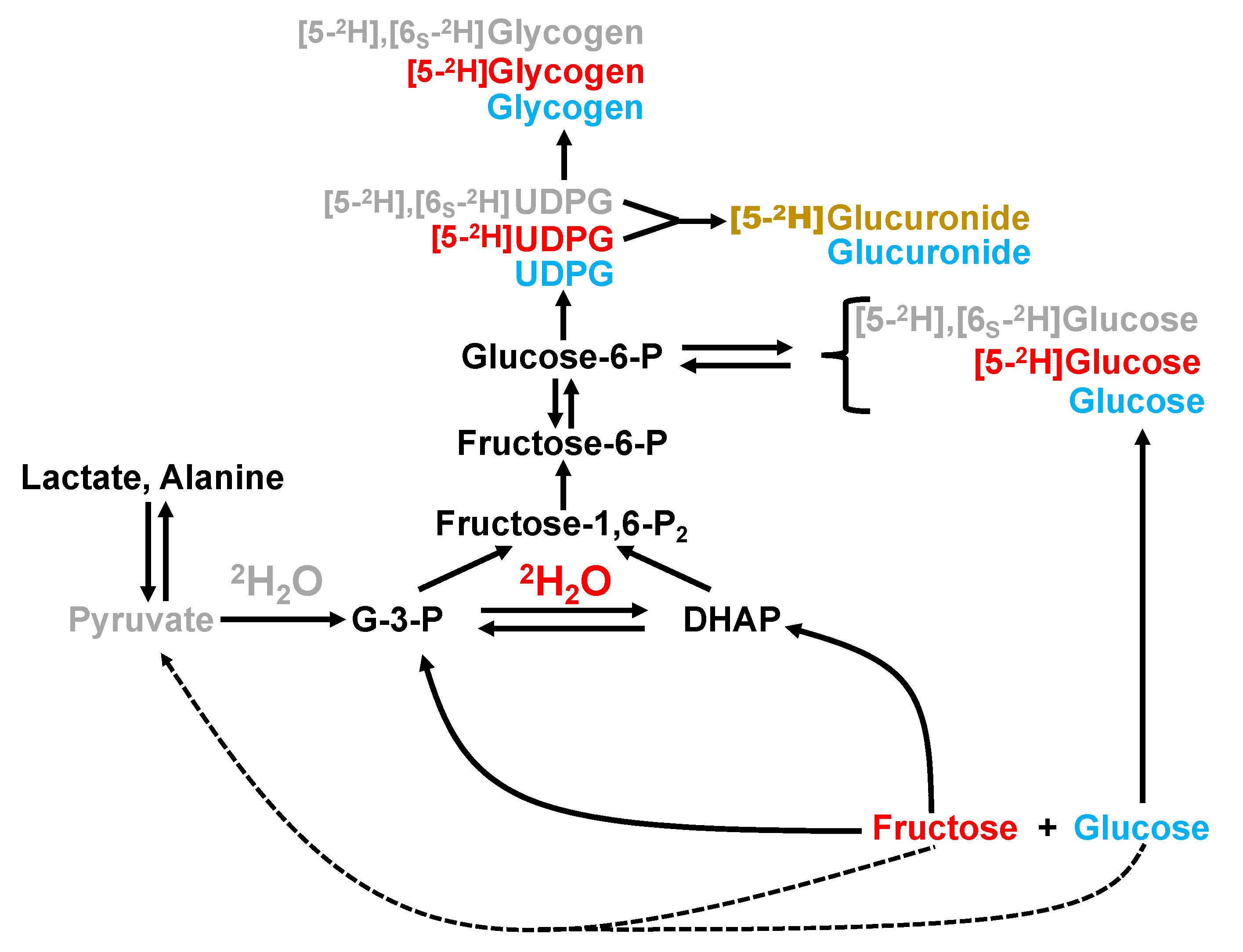
42 label the scheme of glucose catabolism
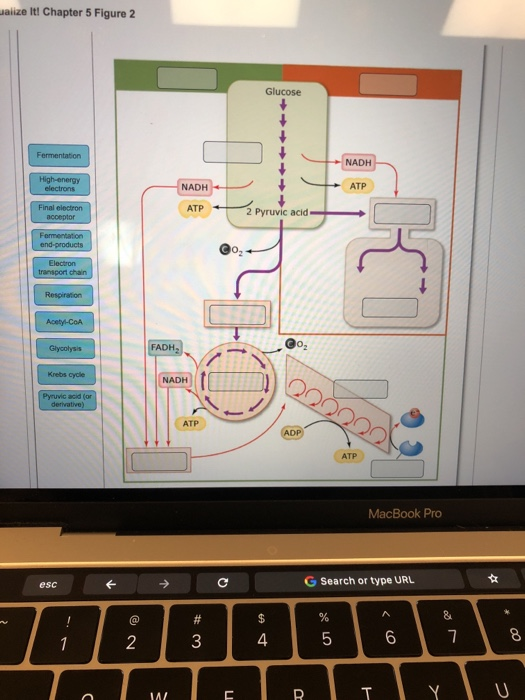
PDF Chapter 5 Endocrine Regulation of Glucose Metabolism plasma glucose concentration, with half-maximal activity not achieved until glucose levels reach the hyperglycemic range; glucokinase is not regulated by glucose-6-phosphate. The phosphorylation of glucose prevents the glucose molecule from leaving the cell. Since, except in liver and kidney, cells lack the ability to remove the phosphate, the Solved Label the image to test your understanding of the - Chegg Label the image to test your understanding of the cellular reactions involved in metabolism. Glucose Catabolism Precursor molecules Anabolism Building blocks Macromolecules Cells Lipids G ya ces Ala Mal Yieldsney Uses energy Uses energy Uses energy Reset This problem has been solved!
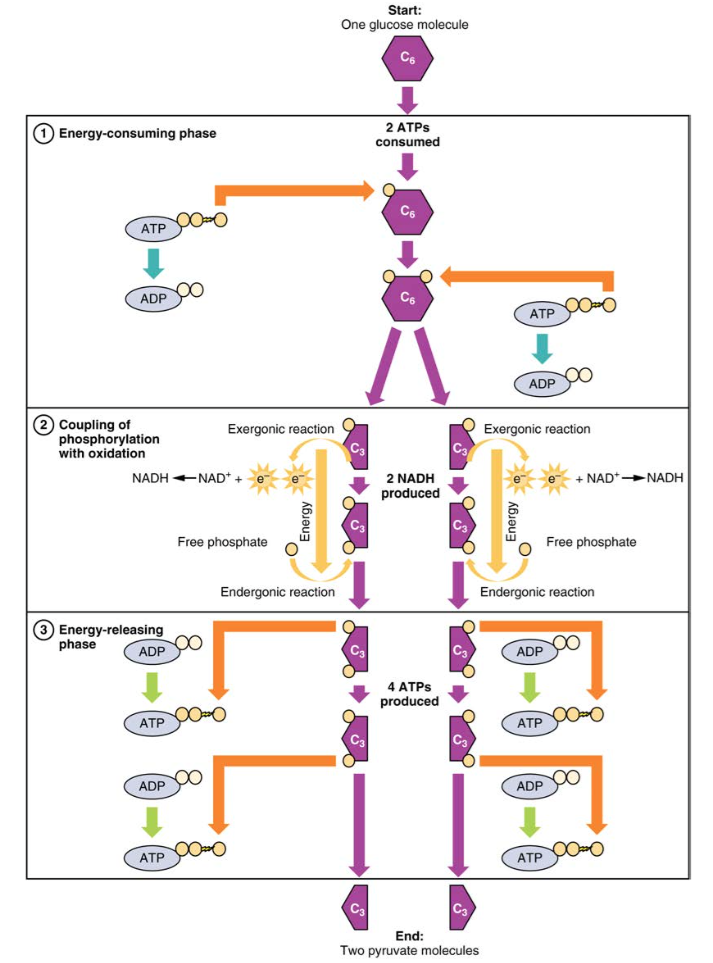
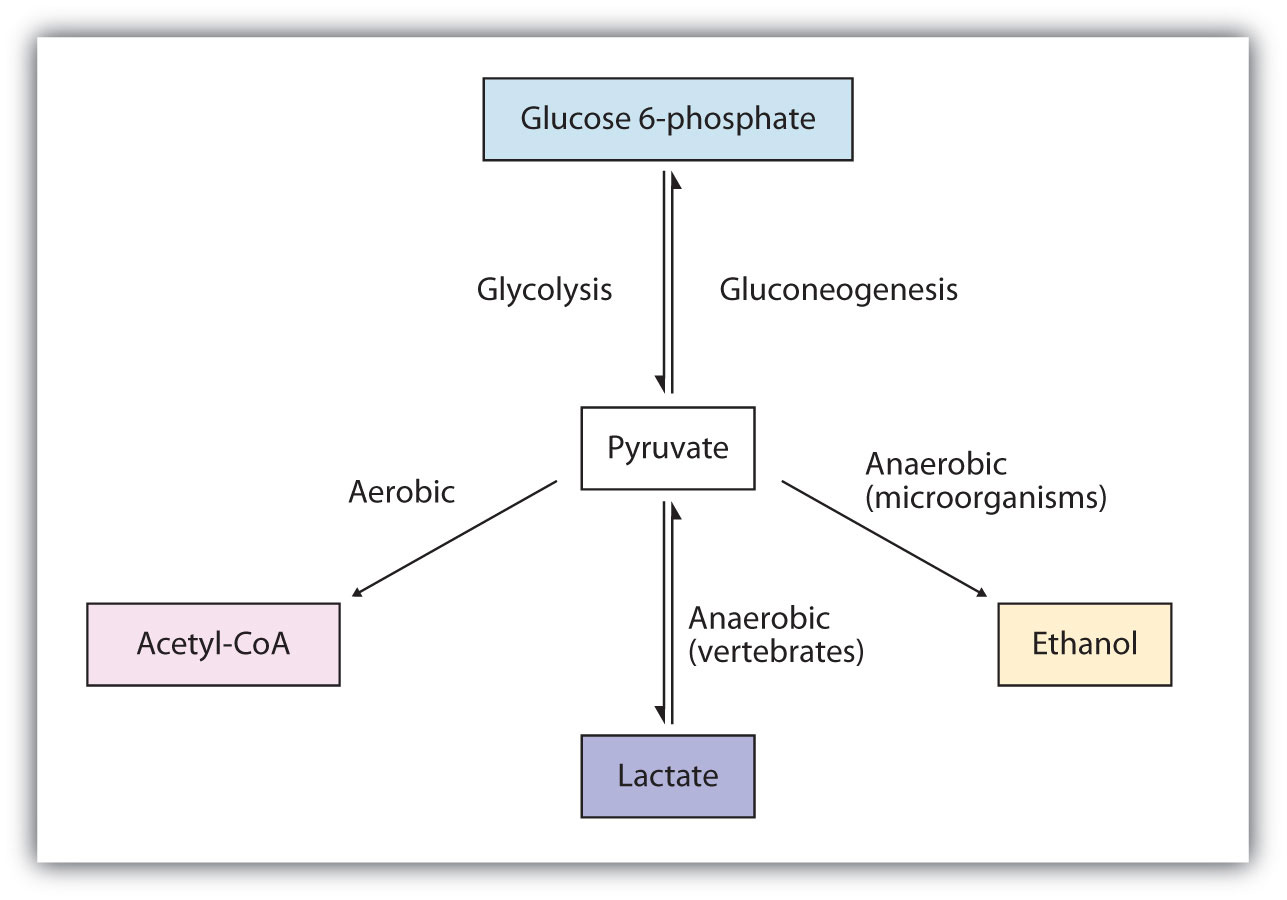
18.4: The Catabolism of Carbohydrates - Chemistry LibreTexts The 10 reactions of glycolysis, summarized in Figures 18.4. 1 and 18.4. 2, can be divided into two phases. In the first 5 reactions—phase I—glucose is broken down into two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. In the last five reactions—phase II—each glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is converted into pyruvate, and ATP is generated.
Label the scheme of glucose catabolism
24.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism - Anatomy & Physiology The first step of carbohydrate catabolism is glycolysis, which produces pyruvate, NADH, and ATP. Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvate can be converted into lactate to keep glycolysis working. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle. 15.9: Overview of Lipid Catabolism - Chemistry LibreTexts Acetyl-CoA is shown in Figure 15.9. 1. The acetyl unit, derived (as we will see) from the breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, is attached to coenzyme A, making the acetyl unit more reactive. Acetyl-CoA is used in a myriad of biochemical pathways. For example, it may be used as the starting material for the biosynthesis of lipids ... Electron Transport Chain | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning Glucose catabolism connects with the pathways that build or break down all other biochemical compounds in cells, and the result is somewhat messier than the ideal situations described thus far. For example, sugars other than glucose are fed into the glycolytic pathway for energy extraction. Moreover, the five-carbon sugars that form nucleic ...
Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. 7.2: Catabolism of Glucose (1)- Stages 1-3 of Cellular Respiration Figure 7.2. 1: The energy investment phase of the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas glycolysis pathway uses two ATP molecules to phosphorylate glucose, forming two glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) molecules. The energy payoff phase harnesses the energy in the G3P molecules, producing four ATP molecules, two NADH molecules, and two pyruvates. Overview of metabolism (article) | Khan Academy Cells are constantly carrying out thousands of chemical reactions needed to keep the cell, and your body as a whole, alive and healthy. These chemical reactions are often linked together in chains, or pathways. All of the chemical reactions that take place inside of a cell are collectively called the cell's metabolism. Microbiology - Mastering Microbiology Homework Chapter 5 ... - Quizlet Created by Kvn4N6 Terms in this set (2) You will label the major processes and steps of glucose catabolism. (See image above) Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. (See image above) Carbohydrate Metabolism | Anatomy and Physiology II - Lumen Learning Describe the process of ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation. Carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. Glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex ...
7.2: Catabolism of Carbohydrates - Biology LibreTexts two NADH molecule, and. two pyruvate molecules. Figure 7.2. 1: The energy investment phase of the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas glycolysis pathway uses two ATP molecules to phosphorylate glucose, forming two glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) molecules. The energy payoff phase harnesses the energy in the G3P molecules, producing four ATP molecules, two ... 6.1: Metabolism - Sugars - Biology LibreTexts The metabolism of glucose, as well as other six carbon sugars (hexoses) begins with the catabolic pathway called glycolysis. In this pathway, sugars are oxidized and broken down into pyruvate molecules. The corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis. Microbiology Connect Quiz #5 Flashcards | Quizlet One reason that the yield of ATP from the catabolism of glucose by aerobic respiration rarely reaches the theoretical maximum is A) that the PMF generated by electron transport is used for functions other than ATP synthesis. B) the TCA cycle intermediates interfere with the activity of ATP synthase. The citric acid cycle | Cellular respiration (article) | Khan Academy Whatever you prefer to call it, the citric cycle is a central driver of cellular respiration. It takes acetyl CoA \text{CoA} CoA start text, C, o, A, end text —produced by the oxidation of pyruvate and originally derived from glucose—as its starting material and, in a series of redox reactions, harvests much of its bond energy in the form of NADH \text{NADH} NADH start text, N, A, D, H ...
Solved C CH:5 Metabolism- carbohydrate catabolism p.133-142 - Chegg Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (7 ratings) Transcribed image text: C CH:5 Metabolism- carbohydrate catabolism p.133-142 ualize It! Chapter 5 Figure 2 Glucose tation NADH ATP ATP 2 Pyruvic acid High-energy Final el end-products or Previous question Next question Frontiers | Flux Connections Between Gluconate Pathway, Glycolysis, and ... FIGURE 1. Schematic of metabolic pathways involved in glucose, fructose, and xylose catabolism in B. megaterium QM B1551. The following pathways are emphasized: gluconate pathway (in red), the Entner-Doudoroff (ED) pathway (in blue), the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) pathway (in light green), the pentose-phosphate (PP) pathway (in black), the fructose uptake pathway (in dark green), and ... ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure and hydrolysis. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions. 20.5: Stage II of Carbohydrate Catabolism - Chemistry LibreTexts Steps in Glycolysis. The 10 reactions of glycolysis, summarized in Figures 20.5. 1 and 20.5. 2, can be divided into two phases. In the first 5 reactions—phase I—glucose is broken down into two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. In the last five reactions—phase II—each glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is converted into pyruvate, and ATP ...
Glycolysis | Cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy Each step is catalyzed by its own specific enzyme, whose name is indicated below the reaction arrow in the diagram below. Step 1. A phosphate group is transferred from \text {ATP} ATP to glucose, making glucose-6-phosphate.
Chapter 5 Mastering Microbiology 2420 McNeil - Quizlet catabolized reduced During a chemical reaction, an organic compound loses an electron to NAD+. An H+ follows the electron and NAD+ becomes NADH. The organic compound that lost the electron... has gained a hydrogen atom. has become more negatively charged. has been reduced.has been oxidized. is an electron acceptor. has been oxidized.
Electron Transport Chain | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning Glucose catabolism connects with the pathways that build or break down all other biochemical compounds in cells, and the result is somewhat messier than the ideal situations described thus far. For example, sugars other than glucose are fed into the glycolytic pathway for energy extraction. Moreover, the five-carbon sugars that form nucleic ...
15.9: Overview of Lipid Catabolism - Chemistry LibreTexts Acetyl-CoA is shown in Figure 15.9. 1. The acetyl unit, derived (as we will see) from the breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, is attached to coenzyme A, making the acetyl unit more reactive. Acetyl-CoA is used in a myriad of biochemical pathways. For example, it may be used as the starting material for the biosynthesis of lipids ...
24.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism - Anatomy & Physiology The first step of carbohydrate catabolism is glycolysis, which produces pyruvate, NADH, and ATP. Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvate can be converted into lactate to keep glycolysis working. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle.
























Post a Comment for "42 label the scheme of glucose catabolism"